What is Perceptron? Single and Multilayer Perceptron
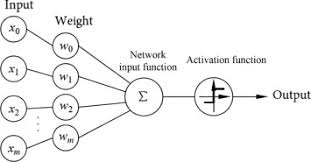
Perceptron A perceptron is one of the earliest and simplest models in machine learning. It is a model that tries to copy the basic behavior of a biological neuron. In biology, a neuron receives signals from other neurons, processes those signals, and then produces its own signal. A perceptron follows the same idea. It receives numerical inputs, multiplies each input by a weight, adds a bias, and then makes a final decision using an activation function. Even though the perceptron is simple, it is very important. It is the building block of many neural network models used today. Without the perceptron, we would not have multilayer perceptrons, deep learning, or modern neural networks. What is a Perceptron? A perceptron is a machine learning model that takes several input values, processes them, and produces a single output. You can imagine a perceptron as a single artificial neuron. The perceptron works by performing the following steps. First, it receives input values. These are usually numbers that represent features of data. For example, if you are trying to classify emails as spam or not spam, your inputs might be numbers that represent words, frequency, or length of the email. Second, each input has a weight. A weight tells the perceptron how important that particular input is. If an input has a high weight, it influences the final decision more strongly. Third, the perceptron multiplies each input by its weight and adds all of these together. It also adds a bias. The bias helps the perceptron shift the decision boundary. Fourth, it uses an activation function. In the original perceptron model, the activation function is a step function. If the total sum is larger than zero, the perceptron outputs one. If the total sum is smaller than or equal to zero, it outputs zero. This means the perceptron performs binary classification. Because the perceptron uses a straight boundary to divide classes, it can only solve problems where the data is linearly separable. If the data requires a curved or complex boundary, the perceptron fails. This limitation is one of the major reasons why researchers moved toward deeper networks. What is a Single Layer Perceptron A single layer perceptron contains only one layer of trainable units. It has an input layer and one output layer. The input layer only passes data forward. The output layer contains one or more perceptrons that make decisions. A single layer perceptron can perform tasks such as simple binary classification and basic pattern recognition. However, it cannot solve problems where the classes overlap in a non linear pattern. For example, it cannot solve the XOR problem because XOR needs a curved boundary and a single perceptron can only draw a straight line as the separating boundary. Even though this model is limited, it is very useful for understanding the foundations of neural networks. It introduces the concepts of training, weights, bias, activation, and linear separation. What is a Multilayer Perceptron in Machine Learning A multilayer perceptron, often called MLP, is a neural network that contains more than one layer of perceptrons. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. Each layer contains several neurons that transform the data. The hidden layers allow the network to learn patterns that are non linear and complex. This is the major difference between a single layer perceptron and a multilayer perceptron. When you add hidden layers and use non linear activation functions, the model becomes much more powerful. It can learn curved boundaries, abstract features, and high level patterns. Because of these extra layers, the multilayer perceptron can solve many problems that a single layer perceptron cannot. Tasks such as image recognition, voice detection, digit classification, and many classical machine learning problems can be solved with multilayer perceptrons. How a Multilayer Perceptron Works A multilayer perceptron has a very clear workflow. This workflow contains two major parts. The first part is forward propagation. The second part is backward propagation with optimization. In forward propagation, the network takes the input data and passes it forward through each layer. At each neuron, the model multiplies the inputs by their weights, adds a bias, and applies an activation function. The activation function introduces non linearity. Without it, multiple layers would still behave like a single linear model. The output of the first hidden layer becomes the input of the next hidden layer. This continues until the data reaches the output layer. The output layer produces the final prediction. If the task is classification, the output may represent class probabilities. If the task is regression, the output may represent a numerical value. After the output is produced, the network calculates the error using a loss function. The loss function measures how far the prediction is from the correct value. Now the second part begins. Backward propagation uses the error and sends it backward through the network. It calculates how much each weight and bias contributed to the error. This is done using the chain rule from calculus. The network then updates the weights in a direction that reduces the error. This process is called gradient descent or an improved version such as Adam, RMSProp, or others. Through many cycles of forward and backward propagation, the multilayer perceptron slowly learns the correct patterns. It adjusts itself until it becomes good at making predictions. Why Multilayer Perceptrons Are Powerful A multilayer perceptron becomes powerful because each hidden layer learns a different type of feature. The first hidden layer learns simple features such as small patterns. The next hidden layer learns combinations of these patterns. Deeper layers learn more abstract representations. This layered learning allows the network to approximate very complex functions. In fact, the universal approximation theorem states that a neural network with at least one hidden layer and non linear activation functions can approximate almost any function to any desired accuracy. This is why multilayer perceptrons are widely used in many fields. They are used in classification, regression, forecasting, signal processing, image